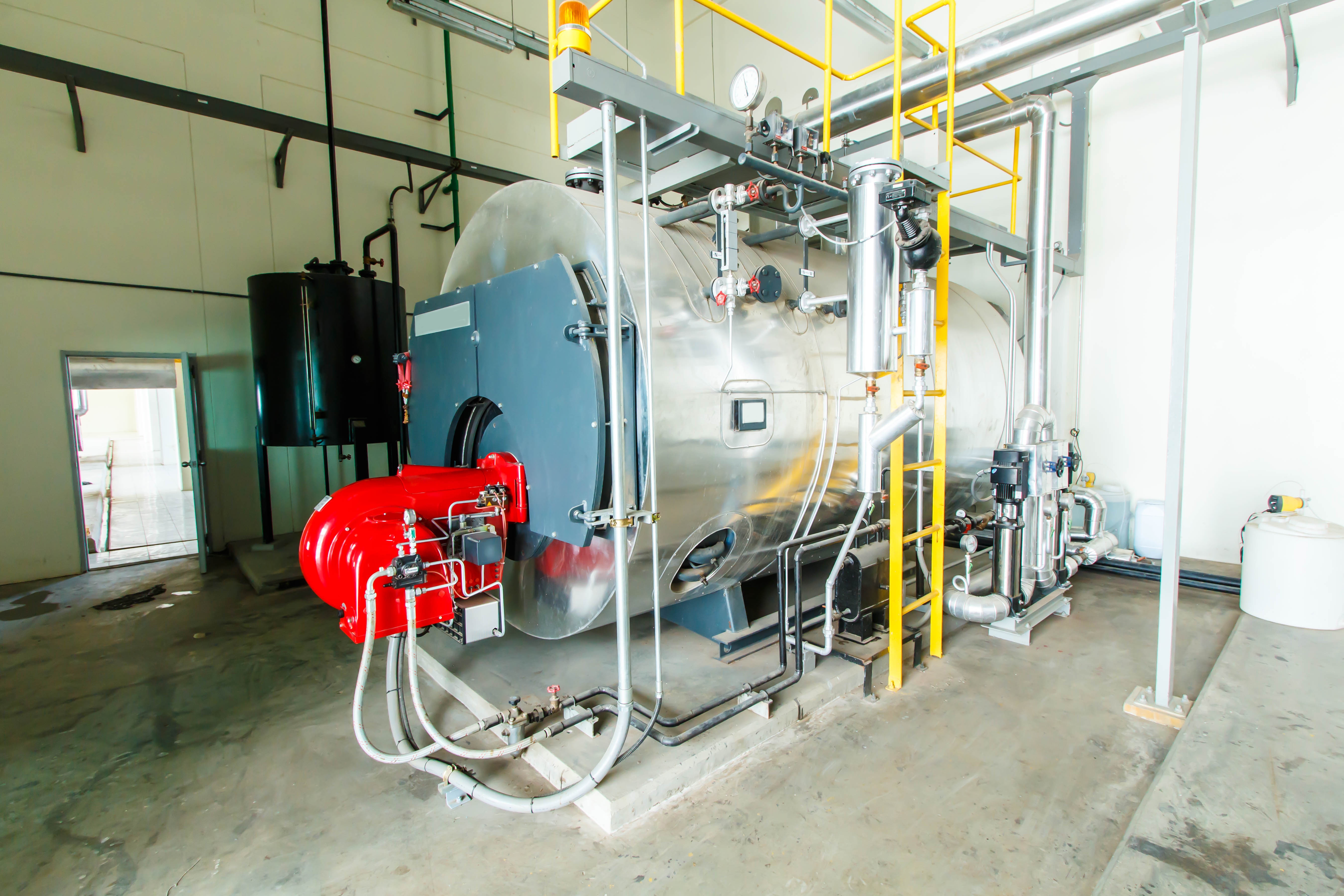
Steam boilers have been with us for a long time. Indeed, you only have to think back to the days of steam locomotives (which followed similar principles as the steam boilers we’re going to discuss here) to remind yourself how enduring they are. Although form and size tend to vary depending on the intended application. Referring to the aforementioned steam locomotives (as well as portable engines and steam-powered road vehicles of yore) and they traditionally facilitated a more compact steam boiler which became an integral part of the means of transportation. Elsewhere the more stationary steam engines, together with industrial installations and power stations typically require significantly more accommodating – and usually individual – steam-generating assemblages. But before we get too far ahead of ourselves, going back to basics we discover that a boiler (or steam generator as such) is a device used to create steam; a process fundamentally achieved courtesy of applying heat energy to water.
Can You Explain the Difference Between Steam Boilers and Hot Water Boilers?
Of course. Not a lot being the answer to this one. You see, with regards to the key operating principles of both steam and hot water boiling equipment, both means lead to pretty much the same end; essentially instigating the heating of water via the burning of a fuel source; thus manifesting the steam element as part and parcel. That being said, while heated water is generally transmitted through boiler tubes, historically steam is circulated round the dedicated facility by the championing of radiators. Meanwhile other core differences worth noting when it comes to comparing steam and hot water boilers include heating points, water level and circulation, cost, accessories, safety, water levels, controls and overall efficiency.
Why do Steam Boilers prove so popular, and What Precursors and Due Diligence Must be adhered to?
Predominantly due to steam boilers offering a cheap and abundant solution when plant engineers necessitate heat transferal by means of water, while both easy storage and transport options add to the appeal. Furthermore many professionals will figure in the high latent heat of evaporation together with equally impressive heat capacity as more decisive factors. However prior to water being utilised specifically for process applications, it must be subjected to dedicated treatment processes so as to guard against the potential onset of scale formation and corrosion compromising the boiler, along with controlling the content of dissolved solids.
With this in mind, duty holders have a legal requirement to manage the threat of exposure to legionella bacteria; a possible danger which could lurk within a cooling system. Ergo, adopting and maintaining a robust and systematically applied house-keeping regime is paramount when ensuring the health and wellbeing of individuals who may interact with the water source. Water treatment programmes must always comply with the relevant industry legislation in place, and uphold the core protocols governed by the following benchmarks;
- Acop L8 (4th Ed.) -Legionnaires' disease: The control of legionella bacteria in water systems: Approved Code of Practice and guidance
- HSG 274 Part 1: The control of legionella bacteria in evaporative cooling systems
- HSG 274 Part 3: The control of legionella bacteria in other risk systems
- BSRIA - Water treatment for closed heating and cooling systems (BG50/2013)
How/Why Would Steam Boilers Require Water Treatment?
Steam boilers come into play in any number of industries, and their presence are commonplace in the manufacturing, chemical processing, food and beverage manufacturing and electrical power-generating sectors. So as you can see their remits are expansive. Problems might arise when steam is produced, not least because dissolved solids can become concentrated and result in deposit formulation inside the confines of the boiler’s infrastructure. As well as having adverse effects on performance and shelf life of the assemblage itself, legionella bacterium could also take root due in the main to the deviation in the temperature of the stored water. As the former concerns lead to poor heat transfer and efficiency losses, the latter could see the materialising of dangerous gases and liquids that not only will corrode the boiler but more worrying still, inflict harm on an individual’s health. Hence why the optimal treatment of boiler feed water is universally considered a vital part of the preventative maintenance program, as opposed to a reactive measure.
Focusing intently on industrial scenarios, and facilities which pursue their manufacturing ends via a calorifier could represent one of the biggest risks of legionella. This is thanks in no small part to the heat transfer coil, which is a crucial – and repeatedly occurring - element which heats large volumes of stored water and as a by-product, encourages steam. When you think about just how many different types of installation requires the habitual storage of hot water (aside from industry; hospitals, hotels, etc all cope with fluctuating daily demand), you can quickly begin to imagine when and where potential legionella flashpoints may arise. Addressing one of the more fail safe ways to reduce the legionella risk, and packaged plate heat exchangers are designed to convey instantaneous hot water, thus minimising the reliance on stored water.
Can We Pinpoint the Main Issues Relating to Steam Boilers and the Potential Legionella Threat?
Beneath we have summarised the most omnipresent steam and boiler problems encountered;
- Scaling – Feed water is often responsible for the build-up of insoluble minerals, which in turn lead to what’s known as scale deposits. These include calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate and magnesium silicate
- Corrosion – The re-oxidation of metals from which water and steam systems are constructed during the exposure to water is referred to as corrosion
- Boiler Water Carryover – Generated by the boiler, steam can often be the vessel by which various solids, liquids or vaporous contaminants are transported
- Sludge –Thick sludge residue can manifest if/when salts and particles of matter in steam boilers are allowed to collect and subsequently congeal after going unnoticed in the feed water over an undefined passage of time
What Course of Action (Incorporating Water Treatment) Do we Recommend When it comes to Steam Boiler Solutions?
During the water-boiling process (and when steam is produced), solids tend to remain in the solution and concentrate. This means that the quantity of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) increases over time. Continued evaporation coaxes the dissolved solids to emerge from the water, and go on to form suspended solids. Or what’s better known as sludge. As this dissolved solids creation ante is upped, the risk of ‘carry over’ grows, in terms of boiler water becoming steam; hence the need to control the magnitude of TDS. Continuous or intermittent blowdown is the process which serves to resolve this potential problem and to effectively eradicate the sludge compound.
Water Cooling is another example of preventative treatment, and as touched on earlier is a much subscribed to method of extracting heat from processes or equipment where water is the sole heat conductor. Both cooling towers and systems’ ability to perform at optimum levels are compromised should critical heat exchange process assemblage suffer damage, which can lead to corrosion, scaling and microbiological contamination (including legionella bacteria). Closed recirculating water systems (the structures of which are often cast from copper, brass, iron, aluminium or stainless steel) also benefit from water cooling processes, as they tend to be more susceptible to corrosion, sludge formation and biofouling.
Otherwise the use of chemicals are prevalent in steam boiler water treatment, with numerous applications including oxygen scavengers, neutralising amines, phosphates, sludge conditioners and alkalinity builders all recruited at different times and instances.